Geotextile Fabrics
Geotextile fabrics, geogrid, and ground cover products – Cherokee has the item you need when you need it.
Geotextile Fabrics FAQs
A geotextile is a permeable textile material used in association with soil to separate, filter, reinforce, protect, or drain.
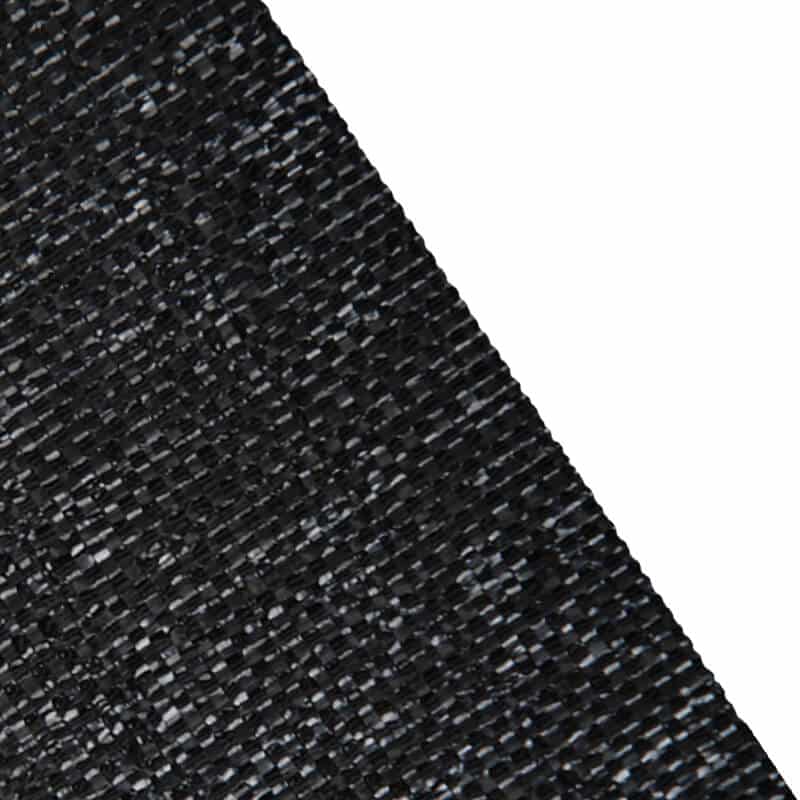
Geotextiles are fabrics used in civil engineering projects to provide strength and stability to a variety of structures. Geotextile materials come in a variety of forms, such as open-mesh, warp-knitted or non-woven fabrics. Each one is crafted to meet specific needs and requirements. The most common types of geotextiles are woven fabric, non-woven fabric, knitted fabric, spunbonded fabric, and braided fabric.
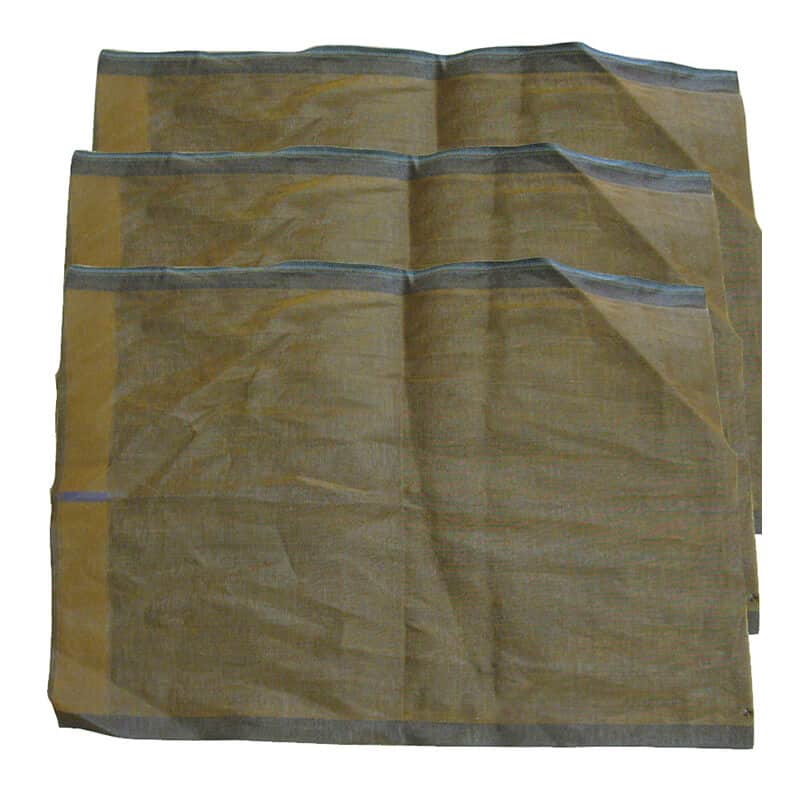
Woven Fabric Geotextile is the most commonly used type of geotextile. It is made from polypropylene or polyester filaments that are woven together into a strong cloth-like material. This type of geotextile is often used for separation purposes such as between soil layers or between aggregate and soil layers.
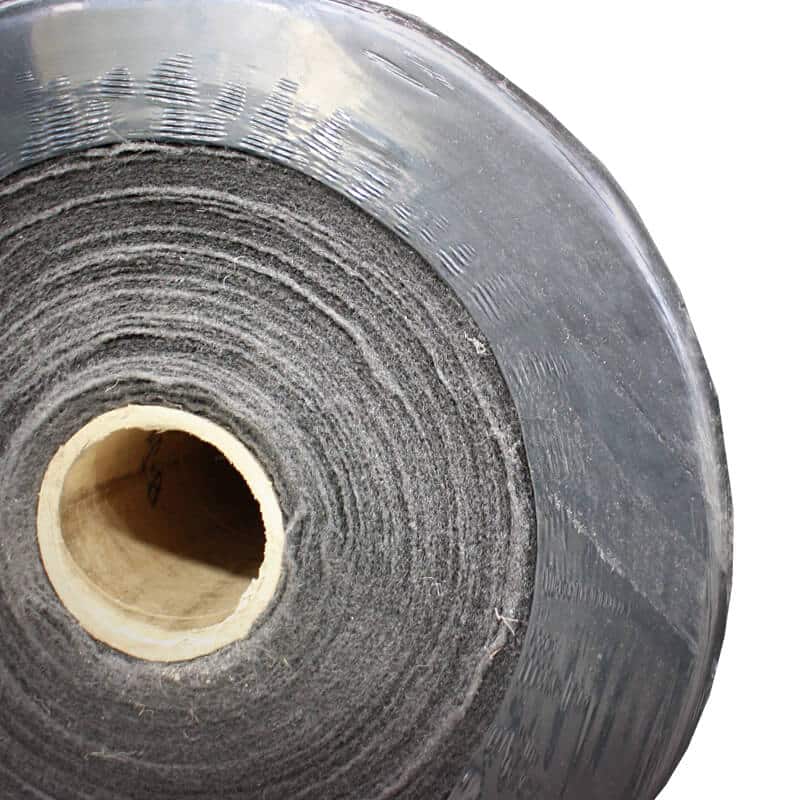
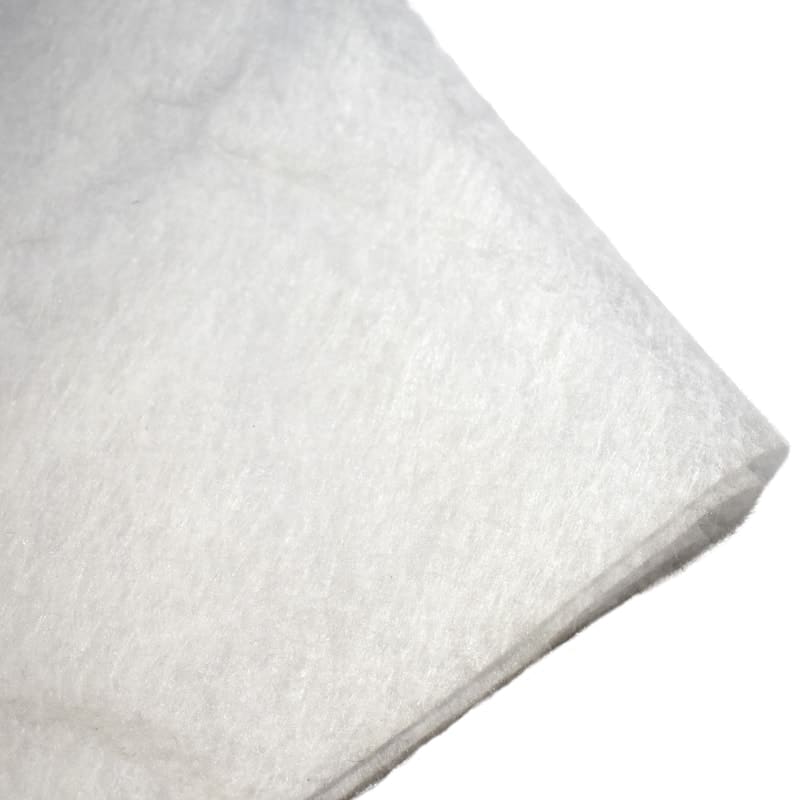
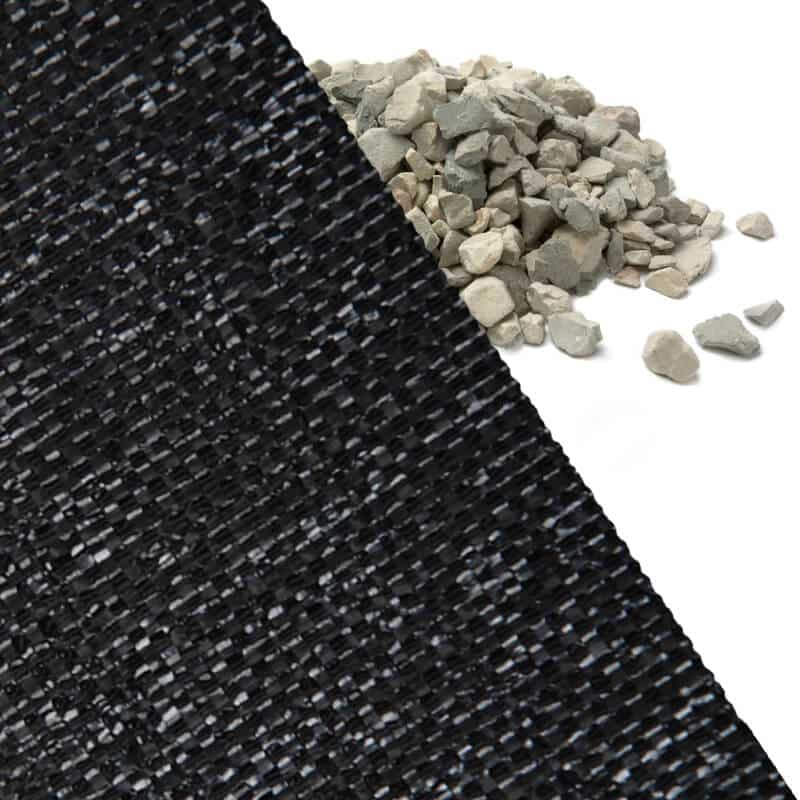
Non-Woven Geotextile is made from randomly oriented fibers that have been bonded together using heat or chemicals. This type of geotextile is often used for filtration purposes such as filtering water from soils or preventing soil particles from entering drainage systems. It can also be used for reinforcement purposes such as reinforcing retaining walls and embankments.
Knitted Geotextile is made by weaving strands of synthetic fibers into a mesh pattern which provides excellent tensile strength and flexibility. This type of geotextile is often used for protection purposes such as preventing erosion along slopes or protecting against abrasion in areas with high traffic loads. It can also be used for drainage purposes such as allowing water to flow through soils while keeping fine particles out of the drainage system.
Spunbonded Geotextiles are made by bonding together synthetic fibers into a sheet-like material which provides excellent puncture resistance and tensile strength. This type of geotextile is often used for separation purposes such as separating different layers of soil or separating aggregate from soils during construction projects.
Braided Geotextiles are made by intertwining multiple strands of synthetic fibers into a strong rope-like material which provides excellent tensile strength and flexibility in both directions along its length and width. This type of geotextile is often used for reinforcement purposes such as reinforcing retaining walls, embankments, bridge abutments, etc., as well as providing additional support to slopes against erosion due to water flow or wave action in coastal areas.
These five types of geotextiles all provide different benefits depending on the application they are being used for but all serve the same purpose: to provide strength and stability to civil engineering projects while protecting them from environmental elements like water flow or wave action in coastal areas.
Geotextiles can be used for many purposes including erosion control, soil stabilization, filtration, separation and drainage.
In erosion control applications, geotextiles are often combined with other materials such as stone or soil to form a protective barrier against the elements. This barrier helps prevent soil from eroding away and can help reduce water runoff. Geotextiles are also used to reinforce slopes and embankments to help stabilize them against the forces of gravity and wind.
Geotextiles can also be used in civil engineering projects such as road construction. They can be placed beneath roads to provide a layer of protection against the elements while still allowing water to pass through. This prevents water from pooling on top of the road surface which can cause damage over time. Geotextiles are also used in retaining walls and dams to prevent seepage and ensure that the structure remains stable over time.
Overall, geotextiles provide an effective solution for many civil engineering projects due to their ability to filter out particles while still allowing water to pass through them, making them ideal for applications where both strength and permeability are needed.
Geotextiles provide many benefits such as increased soil stability, improved drainage, and erosion control. They can also reduce costs associated with construction projects due to their durability and low maintenance requirements.
No, geotextiles are not waterproof but they are permeable which allows water to pass through them while still providing protection from erosion and other environmental factors.
The life span of a geotextile depends on its quality and usage but typically they can last up to 20 years or more when properly installed and maintained. Polypropylene has its own built-in UV inhibitor which makes it the longest-lasting.
Non-woven types of geotextiles tend to be more resistant to tearing than woven fabrics so they may be better suited for applications where strength is needed such as slope stabilization or reinforcement of embankments. Additionally, non-woven fabrics tend to have higher water flow rates than woven fabrics so they may be better suited for drainage applications.